It's fair to say that this week is a festive one. First off, it is Catholic Christmas this Sunday. Second, there won't be much historical context for the news. The most intriguing report of the week focused on the third quarter's GDP in the UK, in particular. This, however, will be the indicator's third estimate for the third quarter. The third estimate is not likely to differ significantly from the first two given that the previous two estimates showed a decrease of 0.2%, even though a 0.5% drop was initially anticipated.
But as I've mentioned in earlier articles, a lot now depends on the interest rates set by the ECB, the Bank of England, and the Fed. The ECB and the Bank of England have not yet been able to approach the Fed rate, although rate-hike cycles are already coming to an end. In the United States, the rate is predicted to increase to 5.25%, while in the European Union, it is currently 2.5% and has already started to decline. Christine Lagarde has never discussed the ultimate rate at which the ECB aspires, and Luis de Guindos said yesterday that he is unsure of the level at which the interest rate must be raised. It sounded as though he was saying, "I don't know to what value the rate will rise," rather than, "I don't know to what value we will be able to raise the rate." The ECB's ambiguity is still half the problem, though.
With great difficulty, the Bank of England in the UK managed to slightly lower inflation after raising the rate for eight straight meetings. In this scenario, the British regulator would need to maintain a pace of 75 basis points of tightening monetary policy, but in December, they dropped to 50 points, and a survey by the Bank of England revealed that the market does not anticipate rates to rise above 4.25%. I'm not sure what kind of survey the British regulator conducted or who took part in it, but bakers with movers were most definitely excluded. Analysts and economists, I suppose. And if they truly do not anticipate another rate increase of more than 75 basis points, this could have the most detrimental effects on the pound, which has been rising recently precisely because the Bank of England is catching up to the Fed, which means it will raise interest rates more strongly and for a longer period.
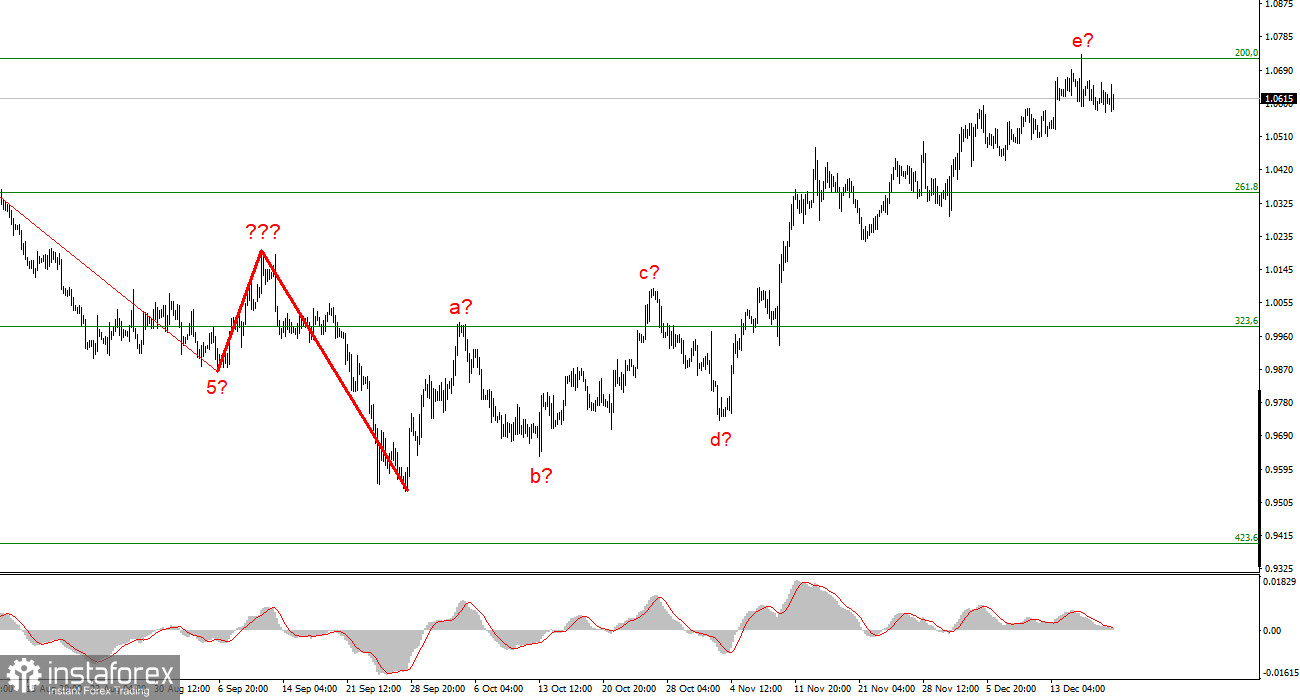
However, in reality, it might be the opposite. Let me remind you that Andrew Bailey signaled the start of a recession in the British economy; consequently, with each new tightening of policy, the regulator runs the risk of making the recession worse. The slowdown and, going forward, the refusal of additional tightening are most likely related to this understanding. Notably, the Bank of England may stop raising rates at the same time as the Fed, which would be in February or March of the following year. The likelihood of completing the construction of an upward section of the trend, in my opinion, has increased. For the next two weeks, we may be in the "holiday trading" phase, but in January 2023, I will once again wait for the development of a minimum correction section of the trend for both of the instruments that I monitor daily.
I conclude from the analysis that the upward trend section's construction has grown more intricate and is almost finished. As a result, I suggest making sales with targets close to the estimated 0.9994 level, or 323.6% Fibonacci. Although there is a strong likelihood that the upward portion of the trend will become even more extended and complicated, there is currently a signal to turn lower.
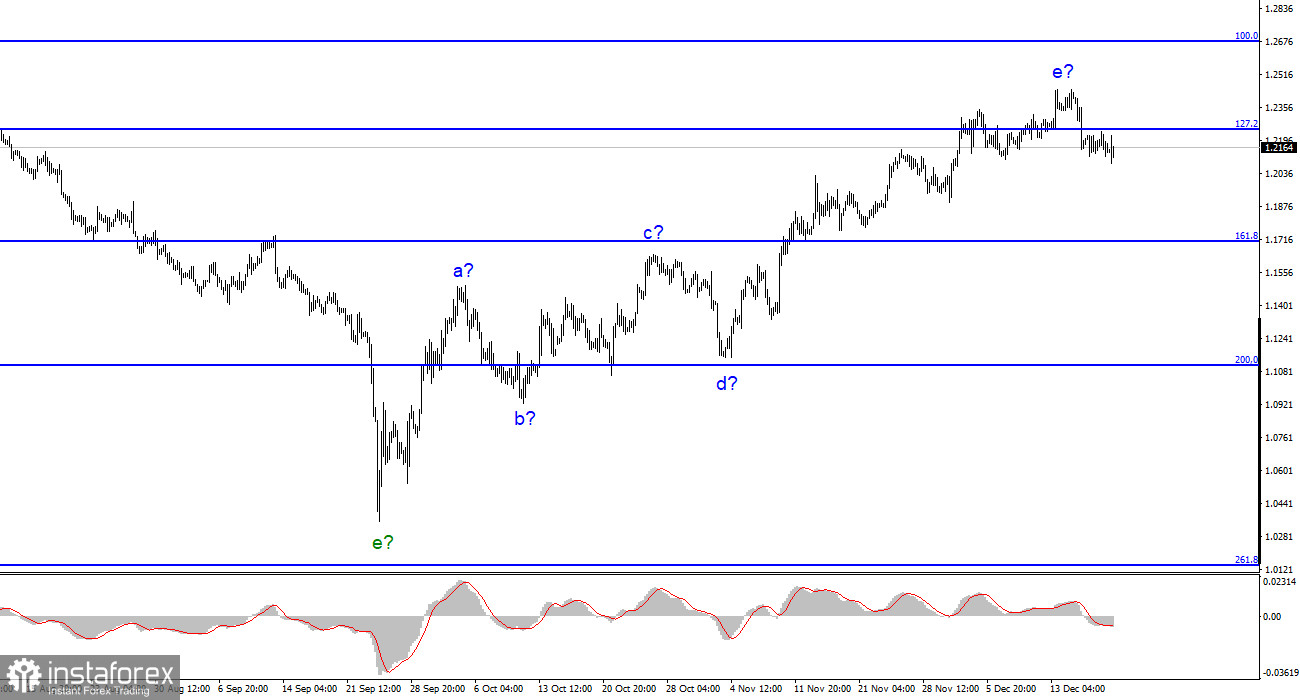
The construction of a new downward trend segment is predicated on the wave pattern of the pound/dollar instrument. Since the wave marking permits the current construction of a downward trend section, I am unable to advise purchasing the instrument. With targets around the 1.1707 mark, or 161.8% Fibonacci, sales are now more accurate. Wave e is likely finished, though it could take on an even longer form.





















