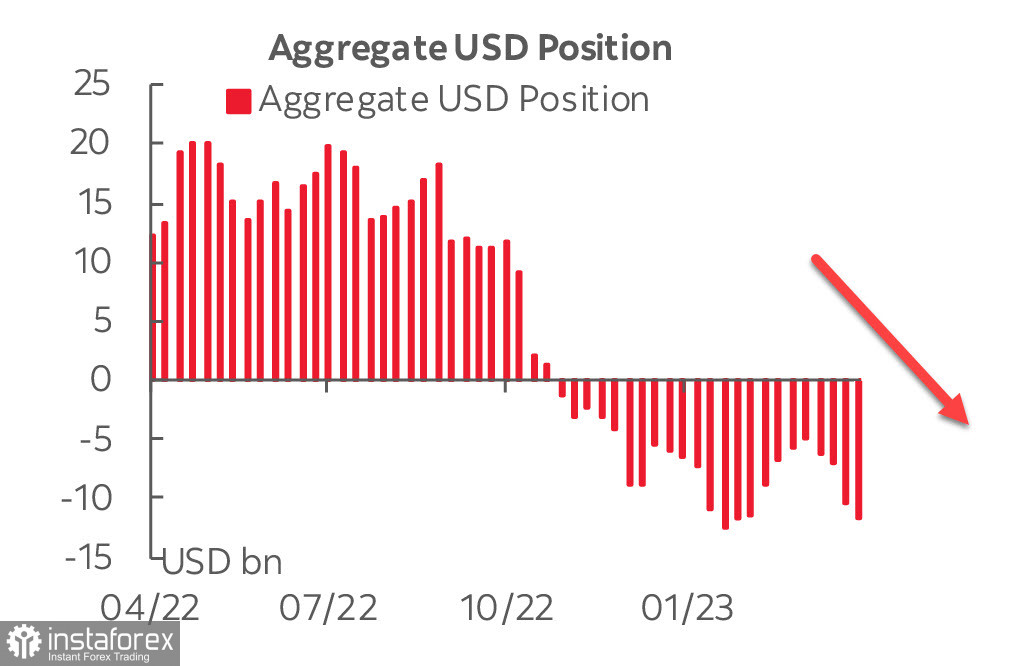
The net short position on the US dollar increased by 1.225 billion to -11.7 billion for the reporting week. The data shows that demand for the dollar is declining, with the aggregate net speculative short position in dollars being the largest since mid-February, with real money accounts increasing their net short position to the highest since mid-2021. Accounts with leverage are selling the dollar less actively, but the trend is the same.
Both US and European PMIs exceeded expectations, primarily due to strong performance in the services sector. The Eurozone composite index stood at 54.4 versus 53.7, services at 56.6 versus an expected 54.5, and manufacturing at 45.5 versus an expected 48.0. The US Composite index was 53.5 versus an expected 51.2, services at 53.7 versus an expected 51.5, and the manufacturing sector at 50.4 versus an expected 49.0.
Tensions in the PMI reports are caused by the increasingly intensifying factor of inflation. The US PMI report states: "Overall output prices rose at the fastest pace for seven months. Firms stated that more accommodative demand conditions allowed them to continue passing through higher interest rates, staff wages, utility bills and material costs to clients." Improved demand conditions support faster growth in April, but also lead to a resurgence of inflationary momentum.
PMI reports show the following. Despite aggressive monetary tightening on both sides of the Atlantic, a number of negative factors have disappeared - the European energy crisis and China's return to active growth. Inflationary pressure remains high, especially given the rapid pace of wage growth. All this does not allow for a quick victory over inflation.
This week, many important reports are coming out from the US (durable goods orders, GDP, personal consumption expenditures), so volatility may increase. More or less strong movements are possible only in case of a reassessment of the Fed's rate outlook, which is unlikely.
EURUSD
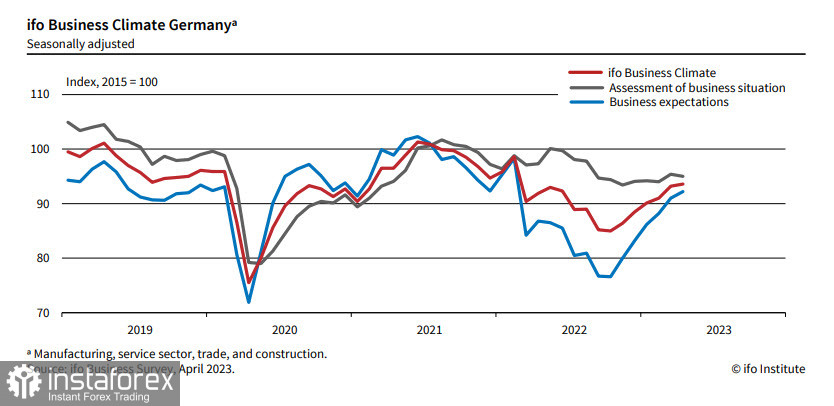
Sentiment in German business has slightly improved. The Ifo business climate index rose to 93.6 points in April compared to 93.2 points in March. This was due to improved company expectations. However, companies rated their current situation as somewhat worse. German business concerns are weakening, but the economy still lacks dynamism. Overall momentum has clearly slowed down, and the positive impulse associated with the lifting of COVID restrictions and the mitigation of the energy crisis is nearing completion.
The European Central Bank is entering a silent mode before the meeting on May 4th. It is expected that the ECB will raise rates in May, but the size of the hike is unclear, as the market forecast gives a 20% probability of a 50 bps hike and 80% for a 25 bps hike. The further dynamics of EURUSD depend on the ECB's actions. A 25 bps hike may lead to a corrective decline in the euro, while a 50 bps hike, on the contrary, will result in a strong bullish momentum.
The net long position in the euro increased by $263 million to $22.542 billion over the reporting week. The increase is small, but the clearly expressed bullish bias remains, and there are no reasons to expect a downward reversal of the euro yet. The calculated price, following the stability in the futures, is also stable, slightly above the long-term average. The momentum is weak, but there is no sign of a reversal trend.
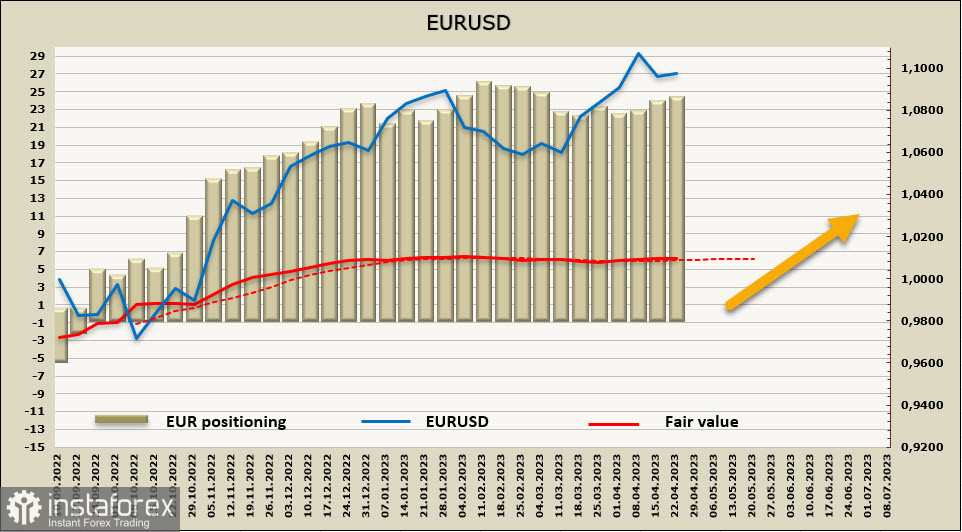
A week earlier, we saw targets of 1.1180 and 1.1270 for EURUSD, and as the pair spent the last few days in consolidation mode, these targets remain relevant. The latest macro data, primarily inflation reports, have barely changed expectations for the future actions of the Fed and ECB. At the moment, the ECB's position looks more hawkish, meaning the yield differential will change in favor of the euro.
GBPUSD
Core retail sales data in the UK were weak, coming in at -1.0% MoM against an expected -0.6%, although they were revised upwards. The statistical service blamed this on poor weather. Meanwhile, a separate survey showed that consumer confidence in the UK rose to its highest level in a year. The April PMI for the service sector was 54.9, higher than the 52.9 forecast, and the same effect is observed in the US and eurozone countries – inflationary pressure remains too high to hope for a quick decline.
In February, inflation growth slowed from 10.4% to 10.1%, significantly higher than forecasts. The NIESR Institute has traditionally prepared three scenarios for the development of inflationary pressure, called "medium," "high," and "very high." A low inflation scenario is not even considered, meaning the choice is between bad and very bad scenarios. The option of a slow slowdown in price growth is still considered as the base case, but it is noted that the likely increase in geopolitical tensions between Russia and NATO, as well as between the US and China, will quickly worsen the overall picture to levels far exceeding those in 2022.
A long position of $101 million has finally been formed for the pound, with an insignificant bias and a weekly change of +$287 million. The calculated price is above the long-term average and is heading upwards.
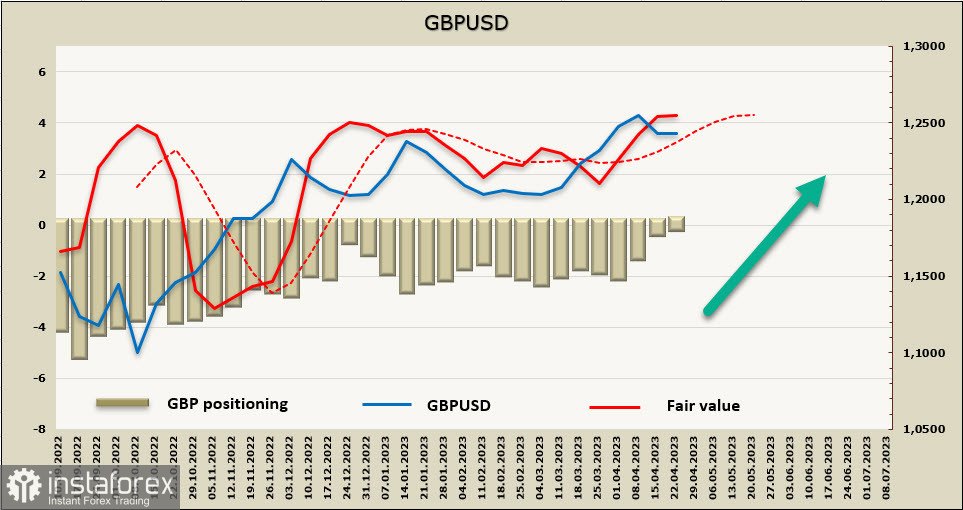
As expected, the pound has stayed above the support at 1.2340, and consolidation is observed. The likelihood of resuming growth is still higher, so we expect that after the consolidation is completed, the pound has a good chance of resuming growth. The nearest target is the local high of 1.2545, with a medium-term target of 1.2750.





















