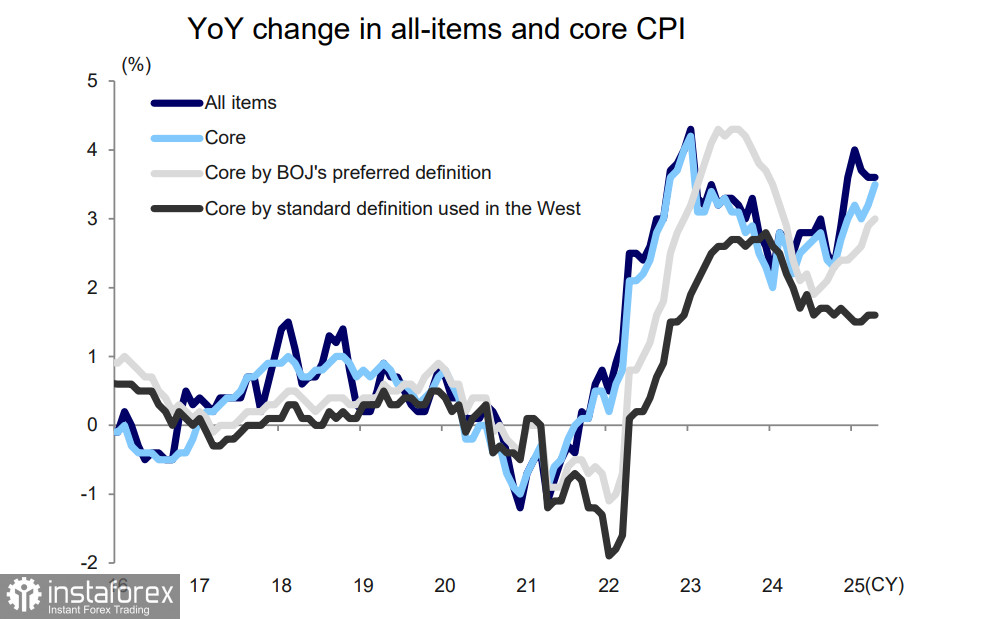
So far, there are no signs of a significant surge in services inflation, and the Bank of Japan remains in wait-and-see mode, observing how U.S.–Japan trade negotiations unfold. The situation is complicated: the economic fallout from Trump's new tariffs has led Japan to lower its growth forecasts, limiting its room to maneuver.
In terms of tariffs, Japan faces a baseline rate of 10%, but key exports like automobiles, steel, and aluminum are taxed at 25%. This is a major blow for Japan, where the automotive sector accounts for 8% of all jobs. Despite being the largest foreign investor in the U.S. economy, Japan has seen no benefit, and the talks have stalled.
We believe the trend toward rate hikes will dominate, as this is the only way to curb inflation—even at the risk of recession. This implies a stronger, not weaker, yen.
Speculative positioning in the yen changed little over the past week, but the accumulated bullish bias remains substantial. However, the fair value has lost directional momentum.
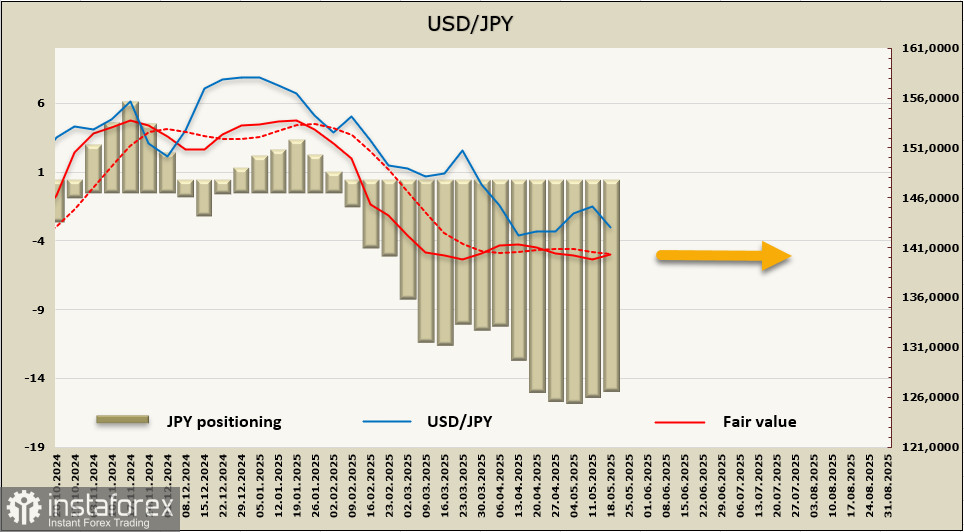
On Friday, the yen strengthened significantly ahead of the close, not so much in response to rising inflation, but to the U.S. House of Representatives passing Trump's "One Big Beautiful Bill" by a single vote. The expected increase in the U.S. debt ceiling by $4 trillion triggered a sharp sell-off in the dollar.
The combination of rising Japanese inflation and expected challenges for the dollar leave the yen with only one path—strengthening. In April, the yen already made an unsuccessful attempt to break below support at 139.49. A reversal in yen appreciation could only occur if trade negotiations lead to a surge in Japanese investment into the U.S., which would prompt yen selling.
Since there's no concrete progress on that front, we expect USD/JPY to make another attempt to break below 139.49, with a long-term target in the 127–129 range.





















