The euro is attempting to resume its upward movement, although not many economic reasons support this scenario. Inflation in May rose in line with the European Central Bank's expectations, which only strengthened the case for continued rate cuts, and business activity indices remained weak. The manufacturing sector stayed at April's level of 49.4 points—showing no improvement at all—while the services sector posted 50 points, slightly better than April's 49.7 points.
Like most other currencies, the euro's rise is largely due to U.S. dollar weakness. Analysts at Nordea Bank believe that the recent declines in both the U.S. dollar and long-term U.S. bonds mark the beginning of a loss of investor confidence in the U.S. In their view, this process is accelerating.
Previously, the yield on long-term U.S. bonds correlated quite closely with the dollar index, but as seen in the chart below, a significant divergence occurred after the announcement of "U.S. Liberation Day."
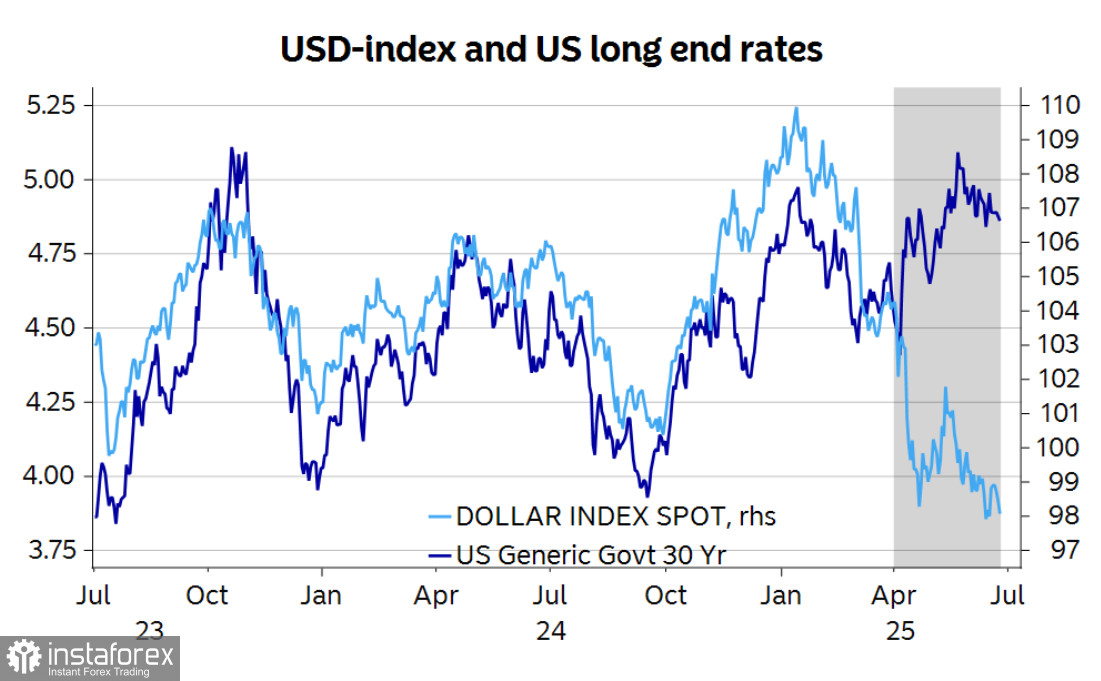
Trump's bill currently under discussion in Congress—more widely known as the Big Beautiful Bill—could support the real economy, but it would create issues for the financial sector. The supply of bonds would increase, which in turn would raise the risk premium.
The Federal Reserve is in no hurry to cut rates, and this ostensibly bullish signal for the dollar has had no effect. At the same time, more opinions are emerging suggesting that the ECB is unlikely to cut rates further—at least, swap markets see no such cut by year-end.
The Big Beautiful Bill being pushed by Trump could lead to higher inflation in the U.S., rising interest rates, and, therefore, higher yields. In the past, this would have been seen as a bullish signal for the dollar since higher yields increase demand for the currency. However, in recent months, the Fed has drastically slowed its pace of rate cuts while the ECB has followed a more predictable path. Despite significantly higher yields in the U.S., this hasn't helped the dollar, and this outcome may indicate that investor confidence in the dollar is waning. As a result, real yields—adjusted for rising risks—are noticeably lower.
No important news is expected from the eurozone until the end of the week. On Friday, the European Commission will publish another forecast package, which traditionally has little effect on financial markets. Only some unexpected factor—not yet priced in by markets—could disrupt the euro's upward trend, and such surprises cannot be ruled out given Trump's unpredictability.
Net long positions on the euro grew by an impressive $1.29 billion during the reporting week, reaching $14.57 billion. The bullish bias in speculative positioning is more than evident, and the estimated price is turning upward again—confirming the prospects for continued EUR/USD growth.
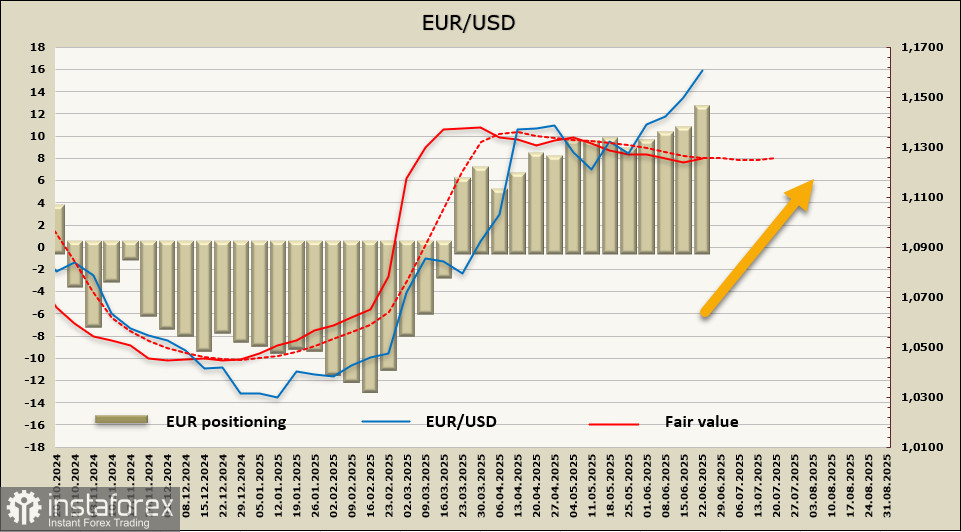
The euro had consolidated over the past two weeks near a 3.5-year high, and there were reasons to expect at least a corrective decline. However, the easing of geopolitical tensions—which had also threatened Europe with reduced oil supply and rising energy costs—has suddenly faded as quickly as it emerged. In the current environment, the euro has once again gained prospects for continued growth. From a technical perspective, the likelihood of a correction remains low, with a long-term target of 1.2350.





















